Allgemein
Caractéristiques principales
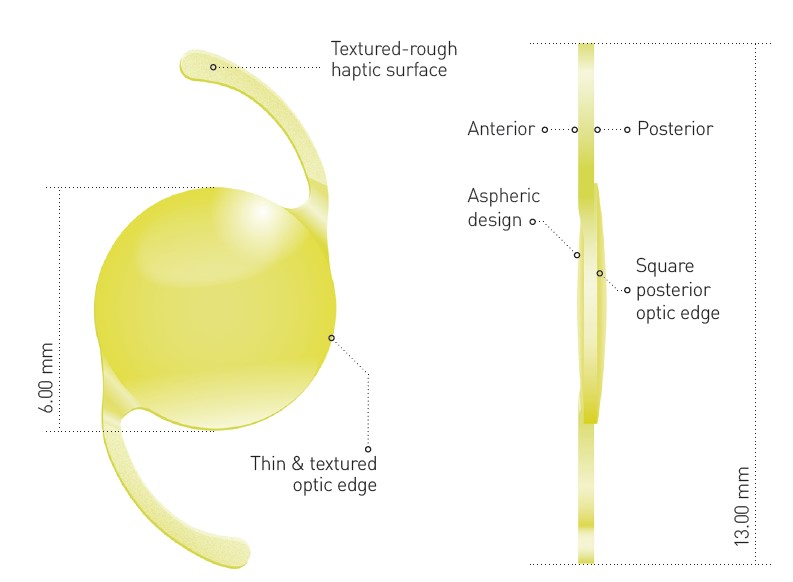
- Profondeur de champ élargie pour soutenir la zone intermédiaire (EDOF)
- Acrylate hydrophobe sans glistening¹, ²
- Optique asphérique pour une meilleure qualité d’image³
- Diamètre extérieur de l’extrémité avant de l’injecteur 1.70 mm
- Les bords texturés de l’optique permettent de réduire la dysphotopsie
- Risque de PCO (Posterior Capsular Opacification) réduit grâce aux bords carrés et un traitement de surface innovant⁴, ⁵
- Haptiques rugueuses texturées
- Transparence à long terme, basé sur des tests in vitro
Vivinex offre aux patients atteints de cataracte une qualité optique exceptionnelle et une vision claire. 1, 2 Les 2 millions d’implants vendus dans le monde entier témoignent de la confiance accordée par les chirurgiens à Vivinex. Vivinex de HOYA est un produit bien établi en Suisse répondants aux exigences les plus élevées : depuis son lancement en 2015, plus de 90 000 Vivinex IOL ont déjà été implantés. La Suisse compte donc plus de patients Vivinex que d’habitants dans la ville de Lucerne !
Bonne reproductibilité et propriétés optimisées des matériaux
Le Dr Philippe Othenin-Girard de Lausanne est un expert de la cataracte et a régulièrement implanté la Vivinex au cours de ces 5 dernières années. Il utilise cet implant avec satisfaction: « La reproductibilité d’implantation est bonne. Les caractéristiques de cet implant que j’apprécie : un matériau hydrophobe sans glistening, des constantes de calcul fiables, un calculateur de lentilles toriques clair et rapide à utiliser, un injecteur qui permet de travailler avec de petites incisions. »
¹ HOYA data on file. DoF-CTM-21-002, HOYA Medical Singapore Pte. Ltd, 2021
² Glistening-free per Miyata scale; study result of the David J Apple International Laboratory for Ocular Pathology, University Hospital Heidelberg. Report on file.
³ Pérez-Merino P, Marcos S. Effect of intraocular lens decentration on image quality tested in a custom model eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44(7):889-896.
⁴ Leydolt, C. et al. (2020): Posterior capsule opacification with two hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses: 3-year results of a randomized trial.
⁵ Matsushima, H. et al. (2006): Active oxygen processing for acrylic intraocular lenses to prevent posterior capsule opacification. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 32 (6), p. 1035–1040. In: American journal of ophthalmology 217 (9), p. 224-231.
⁶ Leydolt, C. et al. (2020): Posterior capsule opacification with two hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses: 3-year results of a randomized trial. In: American journal of ophthalmology.
⁷ Pérez-Merino P, Marcos S. Effect of intraocular lens decentration on image quality tested in a custom model eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44(7):889-896.
² Glistening-free per Miyata scale; study result of the David J Apple International Laboratory for Ocular Pathology, University Hospital Heidelberg. Report on file.
³ Pérez-Merino P, Marcos S. Effect of intraocular lens decentration on image quality tested in a custom model eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44(7):889-896.
⁴ Leydolt, C. et al. (2020): Posterior capsule opacification with two hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses: 3-year results of a randomized trial.
⁵ Matsushima, H. et al. (2006): Active oxygen processing for acrylic intraocular lenses to prevent posterior capsule opacification. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 32 (6), p. 1035–1040. In: American journal of ophthalmology 217 (9), p. 224-231.
⁶ Leydolt, C. et al. (2020): Posterior capsule opacification with two hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses: 3-year results of a randomized trial. In: American journal of ophthalmology.
⁷ Pérez-Merino P, Marcos S. Effect of intraocular lens decentration on image quality tested in a custom model eye. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018;44(7):889-896.
